Context
Just entertainment tools?
Code on the client side can always can be deobfuscated with enough work. Moreover:
- browser DevTools allow the user to observe the deobfuscated code during the execution. Using breakpoints it is possible to tamper the code in any case
- inside the JavaScript engine, the code has to be machine readable therefore the AST (Abstract Syntax Tree) will always be available, and the output bytecode, is still tamperable
code obfuscation refers to obscuring the intended meaning of source or machine code. Therefore, obfuscation can be seen as an approach to increase software security: it deliberately makes code hard to understand and analyze, usually to deter reverse engineering or prevent tampering.
One particular area obfuscation has been applied to in recent years is the client-side security of JavaScript web applications. JavaScript is a high-level interpreted programming language, usually executed on the client side in the browser, meaning the source code of applications is visible for the web browser and the user. To make the code less human readable and the protect it from reverse engineering, JavaScript obfuscators have become available on the web in great numbers. Some of these obfuscators claim to prevent code from being stolen and make it practically impossible to reverse engineer.
This research study and compare 9 different JavaScript obfuscators. JavaScript implementations of three different sorting algorithms - bubble sort, quick sort and radix sort - were then obfuscated using the selected obfuscators and the obfuscation transformations were analyzed
obfuscator.io It offers the largest selection of different obfuscation transformations in this study. In our experiments, we enabled all transformations (with default values), including control-flow flattening, outlining methods, dead code injection, and placing string literals into arrays. Even quite unconventional structures, such as try-catch statements, are added to the code by this obfuscator. Simpler transformations such as variable renaming and encoding strings are also included. obfuscator.io also includes other tricks such as self-defending code (defends against code modification and deobfuscation) and disabling console output, which makes reverse engineering obfuscated code even more toilsome.
BeautifyTools BeautifyTools JavaScript obfuscator reorders and packs the identifiers, keywords and values of the original code in a string, uses some basic string manipulation operations such as replacing and splitting on it and then executes the code using the eval () function. Ironically, this is kind of packing is also a common technique many pieces of malicious JavaScript code use to avoid detection.
JavaScript obfuscator JavaScript obfuscator is basically a simple JavaScript minifier that does not do much to hide the control flow, for example. Identifiers are renamed but values are left intact. However, some well-known names, such as the length property are encoded for additional potency.
JavaScript2img JavaScript2img is an interesting obfuscator that offers a somewhat unconventional way to obfuscate JavaScript: code is embedded within an image, so it cannot be read directly from source code of the web page. The source code that is left is garbled and totally hides the control flow from a human observer. Similar to JavaScript packers, this can be seen as a way to completely rewrite the code into a new from and store it somewhere for later execution.
JSFuck and Esoteric JavaScript obfuscator They both heavily employ JavaScript’s syntactic sugar and their method to obfuscate code does not directly conform to any generic, language independent obfuscation transformations. JSFuck is an esoteric style to write JavaScript, and all code is written using only six characters: [] () ! +. Expressed with just six characters, programs become extremely verbose and unreadable. The borders between statements and other parts of code are completely blurred. Esoteric JavaScript obfuscator uses the same idea but possesses a larger set of characters and, therefore, is also less verbose than JSFuck. It is worth mentioning that these obfuscators have been done more for recreational obfuscation than for protecting programs, but they can still be used to render JavaScript code unreadable.
UglifyJS UglifyJS is a highly effective minifying code compressor, not really meant to intentionally make code harder to read. However, it does more than renaming variables and removing white spaces and often changes the control flow of the target program in the progress. It uses the abstract syntax tree to representation to make various optimizations to the code, such as joining consecutive statements into sequences using the comma operator, discarding unused variables, and optimizing conditional expressions.
PHP JavaScript Obfuscator PHP JavaScript Obfuscator works somewhat similarly to BeautifyTools JavaScript obfuscator in the sense that it also packs the code and then executes it using the eval () function. However, the keywords in the original code are not visible in the clear but the whole code is encoded.
Aaencode aaencode’s idea is somewhat similar to JSFuck. It uses lots of special characters and encodes Javascript code so that it looks like emoticons. This method of obfuscation also completely hides the control flow, identifiers and values.
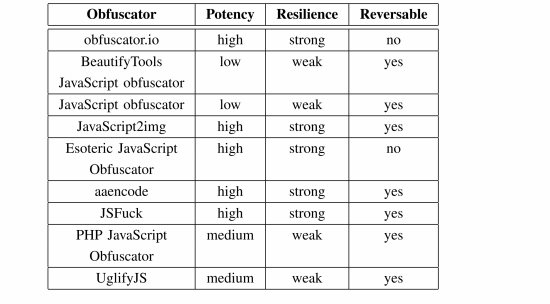
Estimated resiliency, potency and reversibility
Improving obfuscation strength
- More complex transformations. There are still many resilient obfuscation transformations that do not seem to be actively used by the current obfuscators. Examples include obfuscating the data flow using opaque predicates, parallelizing code and splitting variables in a complex manner.
- Combining several transformations. While obfuscator.io seems to take good steps towards combining several resilient obfuscation transformations, even more complex combinations could be developed for better resilience. The theory of combining several different obfuscation transformations and the order in which the specific transformations can be applied have already been discussed in the existing literature.
- Diversification. While some of the obfuscators seem to add some randomness to their obfuscations each time, this is not a common practice. Obfuscated code should be uniquely obfuscated (diversified) so that the same program is not obfuscated in the same way on many different websites, for example. Unique randomization can be added to obfuscation transformations and the order in which they are applied. This makes it harder to attack the obfuscated code because the same attack method does not work against all diversified versions. A web application could be re-obfuscated on each load. This, of course, would require the web page to request a new obfuscation from the server each time it is loaded.
- Dynamic obfuscation. An even better option would be dynamic run-time obfuscation that would change the code of the program on the fly by requesting new obfuscated blocks of the code from the server and continuously replacing parts of the program. This kind of a dynamic change in the program structure is often referred to as Moving Target Defence.