Main concepts
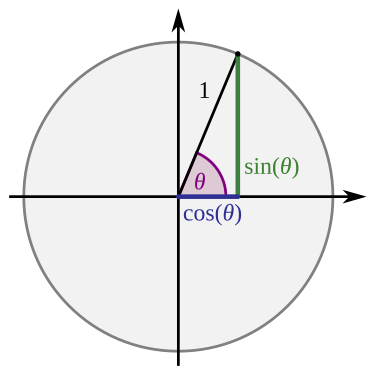
Sine and cosine are trigonometric functions used to get the specific position on an unitary circumference. These functions are often used to translate radians to a value that represent a position on a ideal circle, with ray = 1 and center in (0, 0).
Math.cos()
Given the radian angle, this function identifies the horizontal placement on a unitary circle
Math.sin()
Given the radian angle, this function identifies the vertical placement on a unitary circle
An example on HTML canvas DOM element:
const angle = 45;
const rad = angle * Math.PI / 180;
const x = centerX + radius * Math.cos(rad);
const y = centerY + radius * Math.sin(rad);
const canvas = document.createElement('canvas');
dv.el('div', canvas);
const ctx = canvas.getContext('2d');
// canvas
canvas.width = 300;
canvas.height = 300;
const radius = canvas.width * 0.5 - 10;
const centerX = canvas.width / 2;
const centerY = canvas.height / 2;
// hand
const angle = 45;
const rad = angle * Math.PI / 180;
const x = centerX + radius * Math.cos(rad);
const y = centerY + radius * Math.sin(rad);
// draw
ctx.fillStyle = 'white';
ctx.fillRect(0, 0, canvas.width, canvas.height);
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.arc(centerX, centerY, radius, 0, 2 * Math.PI);
ctx.strokeStyle = 'black';
ctx.stroke();
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(centerX, centerY);
ctx.lineTo(x, y);
ctx.stroke();