Definition
Paywalls are a broad term for monetization systems where visitors are charged subscription fees to access site content, sometimes after being able to sample a small amount of content for free.
The upsides of paywall systems:
- they promise to enable the continued creation of high-quality content
Risks and implications of walled web:
- reducing societal access to news and information
- privacy harms of the increased user tracking needed to enforce paywalls (the engagement of the user with the platform is tracked: how much time the user spend on the platform, how many article he reads, etc)
- paywall may introduce a class system on the web, where high-quality content is reserved to rich people
Google, Facebook and Apple, build platforms to provide or support paywall services
Types of paywalls
Hard paywalls: the subscription is required before visitor can access the content (e.g., Netflix business model)
Soft or metered paywalls: a freemium business model is implemented, where free contents are combined with premium content, or where all the content is available but for a short amount of time
- in most of these scenario, a JavaScript snippet measure either the number of articles a user has accessed or the time a user spends in browsing the website's content
Paywall prevalence and distribution
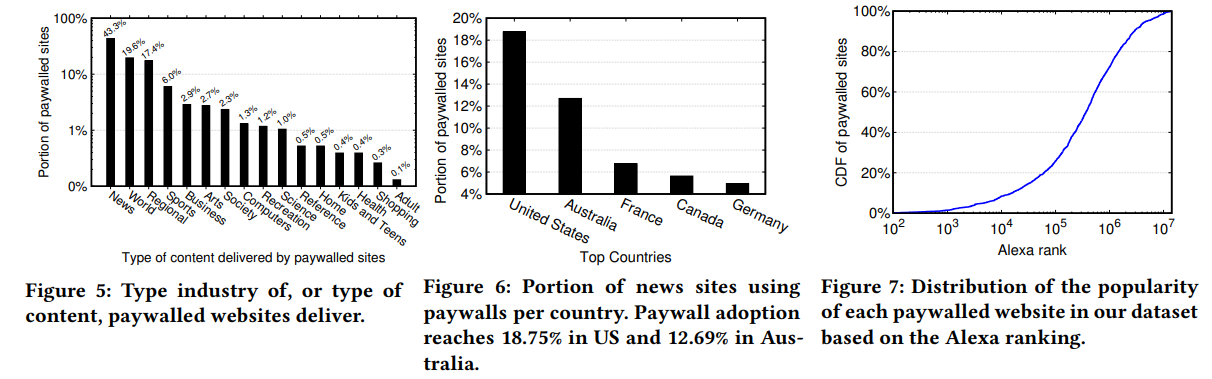
- Site types: news content (80.3%)
- Country: US, Australia, France, Canada, Germany (the most expensive paywalls are also in Germany)
- Popularity of paywalled-websites: only 8.54% of paywall-using sites are among the 10,000 most popular sites on the web
Paywall providers: risks of a monopoly
A significant number of sites rely on third-parties for their paywall implementation. Most popular paywall-as-a-service: Piano (23.5%) and Tecnavia (21%). This monopoly is significant because:
- affect amount of income content-makers can receive
- make large scale bypass easier
- privacy implication in having a small number of providers tracking users
Prevalence of paywalls types:
- soft paywalls (66.7%)
- hard paywalls (15.6%)
- hybrid approach (16.6%): machine learning is used to classify an article as locked, or not
Enforcement mechanism
- truncating article text
- obfuscating the article with popups
- redirecting users to a subscription page (less frequent, 7.3%)
Effects on the UX Users view less pages on paywalled sites, stay for shorter periods of time and link to pages less. Interestingly, we did not see a significantly difference to the bounce rate between paywalled and non-paywalled sites
[![[error]]] Paywalls and privacy People do not generally receive a tracker free version of site content when paying for subscriptions. Instead, paywall systems seem to serve as an additional monetization mechanism on top of existing, privacy harming, ad systems
References
(Papadopoulos, Snyder, et al., 2020) (Kim, Wang, Kwon, et al., 2023)